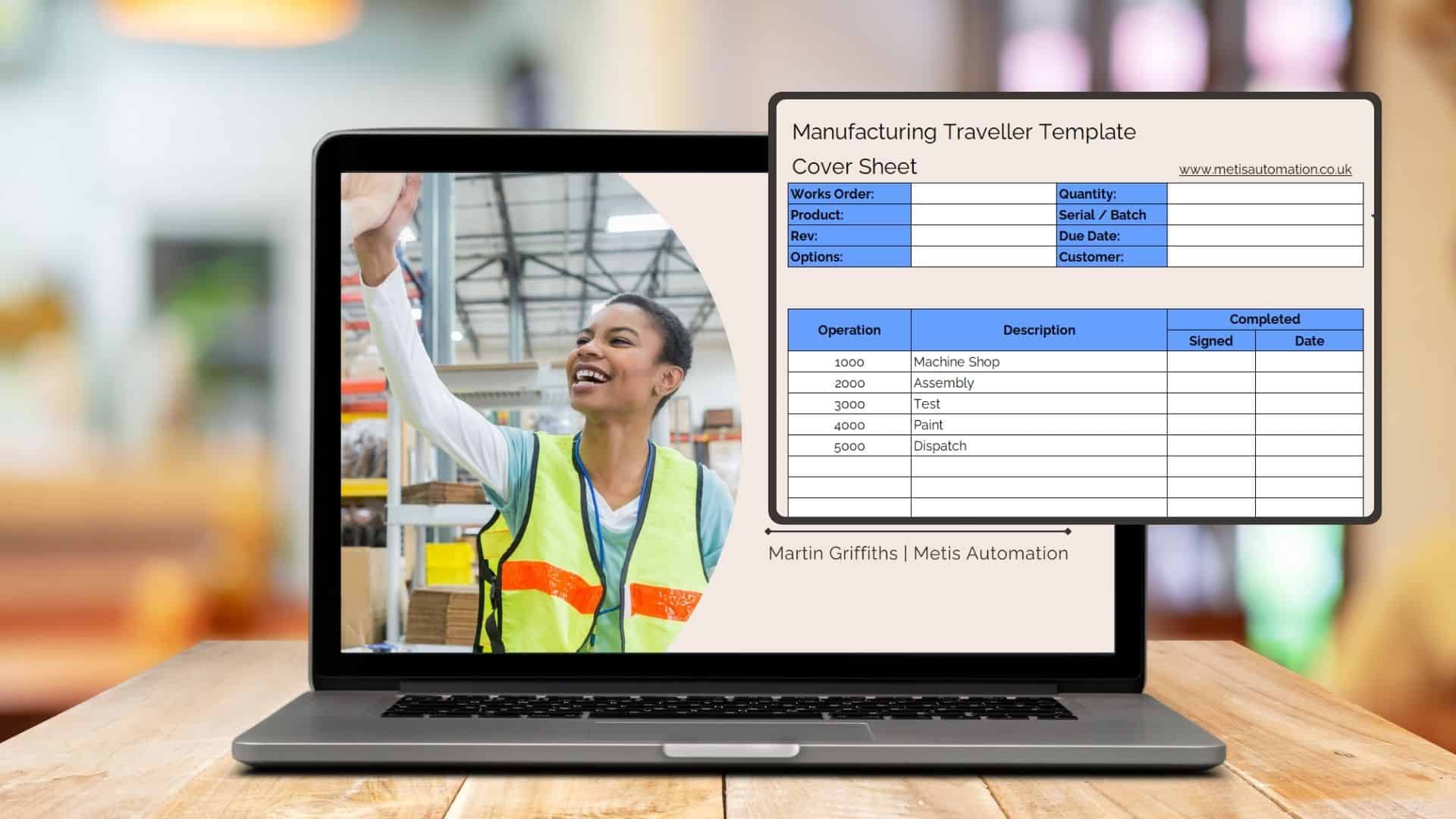
Machine downtime can have a big influence on everything in your manufacturing process. In fact, not only does it affect the manufacturing process, but it can take a toll on your business operations as a whole.
If you’ve experienced losses due to machine downtime, you’re not alone! Many companies around the world lose billions each year due to downtime. Machine downtime is an unintended reduction or halt in a production process or machine. There are numerous reasons why this can happen, but the main question is, how can you reduce or even avoid machine downtime?
We have outlined five key steps you can take to address machine downtime systematically to ensure your processes run optimally and effectively. Watch the video below to learn how you can reduce the risk of machine downtime in five simple steps.
Categorise the reasons
Start by either giving your machine operators a logbook or an Excel spreadsheet. Then over a 24 hour, week-long or month-long period, categorise when it stops, and what happened. They may use descriptive language to start with, so you’ll need to process them into categories such as filter changes, tooling problems and other machine-related problems.
So, capture the data from your operators first, then categorise and organise the various issues. From that, you can also quantify the number of downtimes for filter changes, versus the period of downtime for being low on materials. Based on these quantities sort them from high priority to low, and figure out what to focus on first. Go through them one at a time, eliminating and tackling the issues you’ve found.
Get to the root cause
Once you’ve categorised and prioritised what issues you’re going to address and in what order, you need to understand what the root cause is.
So, if it’s downtime for an unexpected filter change – use a methodology like the Five Whys. Ask, for example, “why did it take two hours to do a filter change”? The answer may be that the filter was in maintenance and had to be requested, and there’s a whole process around that. So the next “why” is “why is there such a lengthy process for requesting a filter for maintenance”?
Keep on drilling down the “whys” to ensure any solution you come up with, addresses the real underlying issues. Make sure that it’s not likely to happen again. If you just resolve the most obvious question, you’re likely to only come up with a solution that’s just a sticking plaster, which won’t work in the long term.
Monitoring
Take the example of replacing the filter. After looking at some of the issues as to why it took so long to get a replacement filter, the solution may be to have a storage of spare filters lineside, rather than in maintenance stock, so the process is quicker. The next step would be to start monitoring data and collecting data on your machine, so you can predict when a filter change is going to be needed in the future.
There’s a number of different ways to do that. A simple way might be to take a measurement on the machine, maybe a temperature or a pressure, at this start or the end of every shift. Use an Excel spreadsheet to plot over time, and use it to understand at what point you need to make a filter change. rather than waiting until the machine tells you it needs doing.
Use data to help you to be more proactive, either using a simple method like a spreadsheet or alternatively, a more fancy method such as using a sensor. Log it over time in an automated dashboard, using some software with rules that tell you when to do things.
Training
Whatever lessons that you learn from using these methods, make sure you get the operators of those machines on board with that. Train them in the processes and actions required to keep their machine running as optimally as possible.
You can use a number of different sources such as taking advice from the service engineers or the manufacturer of the machine to using any kind of internally developed techniques.
Monitor trends, make sure your machine operators are as knowledgeable on them as possible and that they understand the consequence of the methods used.
Preventative maintenance
The machine manufacturer will probably have given you some suggested scheduled maintenance tasks to do. You need to either make sure that they’re on a support contract and are coming in and doing that, monthly, six-monthly, 12 monthly, or whatever the period is.
You should put some kind of fool-proof internal preventative maintenance schedule in place to make sure that either the machine operator or your maintenance guys are coming in and doing these tasks before it gets to a state that the machine shuts down or hits a warning or alarm telling you something needs changing.
Like I mentioned previously, do that proactively. Do it at the end of the week or on the weekends or any other machine downtime so it doesn’t impact the productivity of the machines.
Summary
So the five suggestions for reducing machine downtime are:
- Categorize the things and prioritize the things that are causing machine downtime.
- Identify the root cause of each of the issues.
- Collect some data and monitor the machine going forward to understand what things you can learn from the machine, to tell you when to when you need to do things.
- Keep your operators trained on as the processes change and make sure they know exactly what they should be doing.
- Keep proactive and do predictive maintenance and preventative maintenance to make sure that any downtime is scheduled and won’t impact productivity.
Unleash the Power of Digital Manufacturing
Download our free Digital Transformation Starter Kit to set the gold standard for operational clarity and excellence.